The effect of primordial mass segregation on the size scale of globular clusters
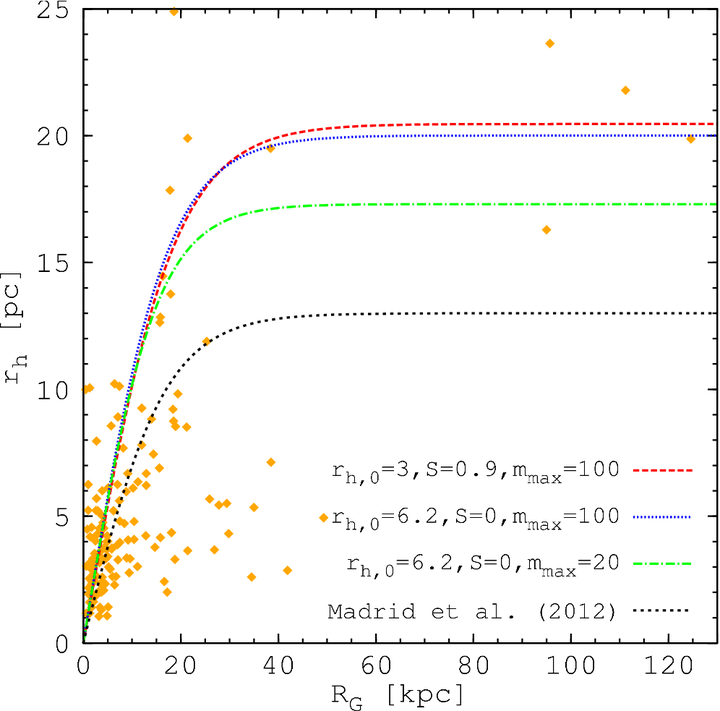 3D half-mass radius and galactocentric distance of the MW GC population taken from Harris (2010). Like in Fig. 5, different lines show the maximum of the 3D half-mass radius of the simulated star clusters versus galactocentric distances after a Hubble time of evolution.
3D half-mass radius and galactocentric distance of the MW GC population taken from Harris (2010). Like in Fig. 5, different lines show the maximum of the 3D half-mass radius of the simulated star clusters versus galactocentric distances after a Hubble time of evolution.Abstract
We use direct N-body calculations to investigate the impact of primordial mass segregation on the size scale and mass-loss rate of star clusters in a galactic tidal field. We run a set of simulations of clusters with varying degrees of primordial mass segregation at various galactocentric radii and show that, in primordially segregated clusters, the early, impulsive mass-loss from stellar evolution of the most massive stars in the innermost regions of the cluster leads to a stronger expansion than for initially non-segregated clusters. Therefore, models in stronger tidal fields dissolve faster due to an enhanced flux of stars over the tidal boundary. Throughout their lifetimes, the segregated clusters are more extended by a factor of about 2, suggesting that (at least) some of the very extended globular clusters in the outer halo of the Milky Way may have been born with primordial mass segregation. We finally derive a relation between star–cluster dissolution time, Tdiss, and galactocentric radius, RG, and show how it depends on the degree of primordial mass segregation.